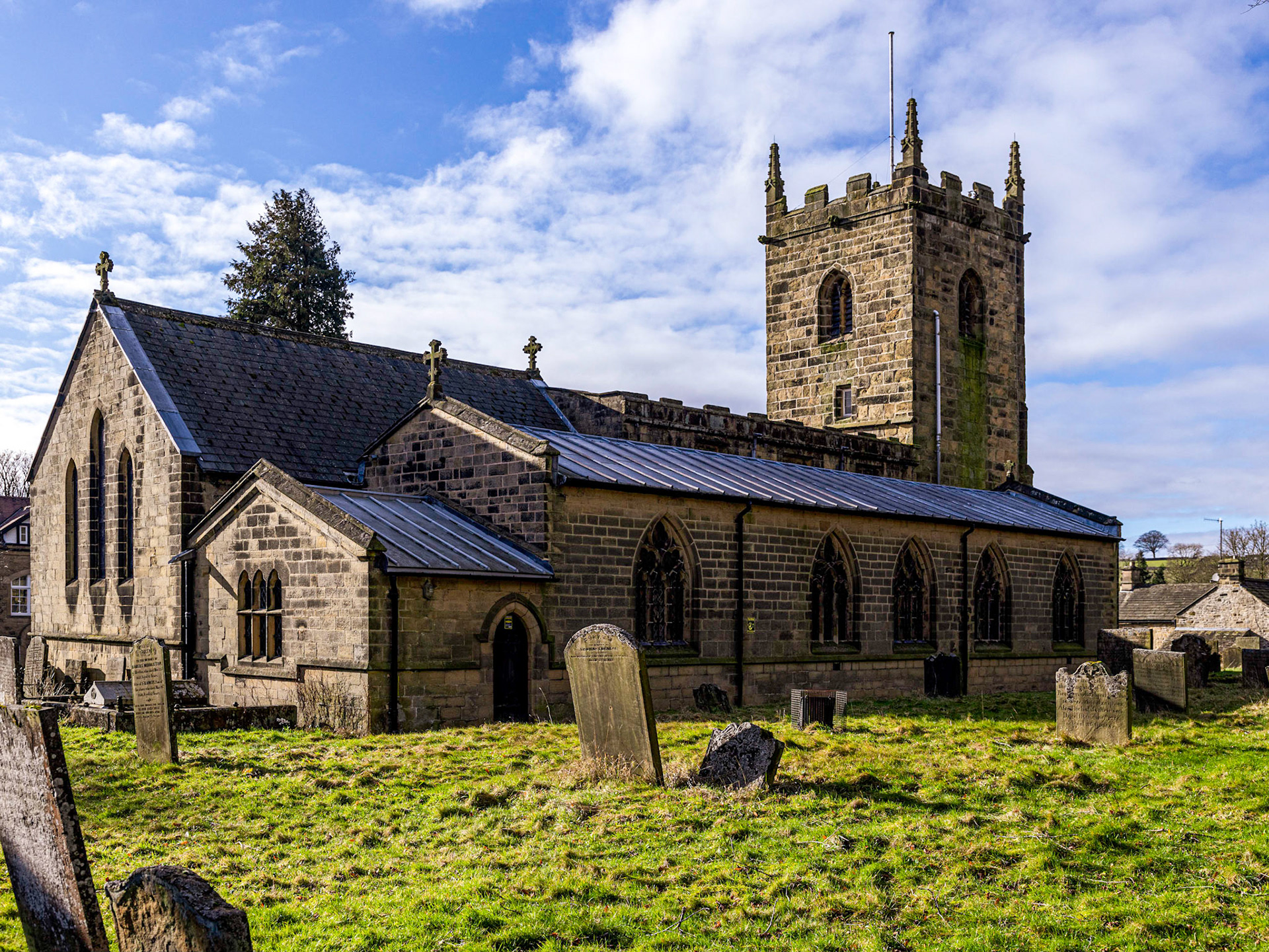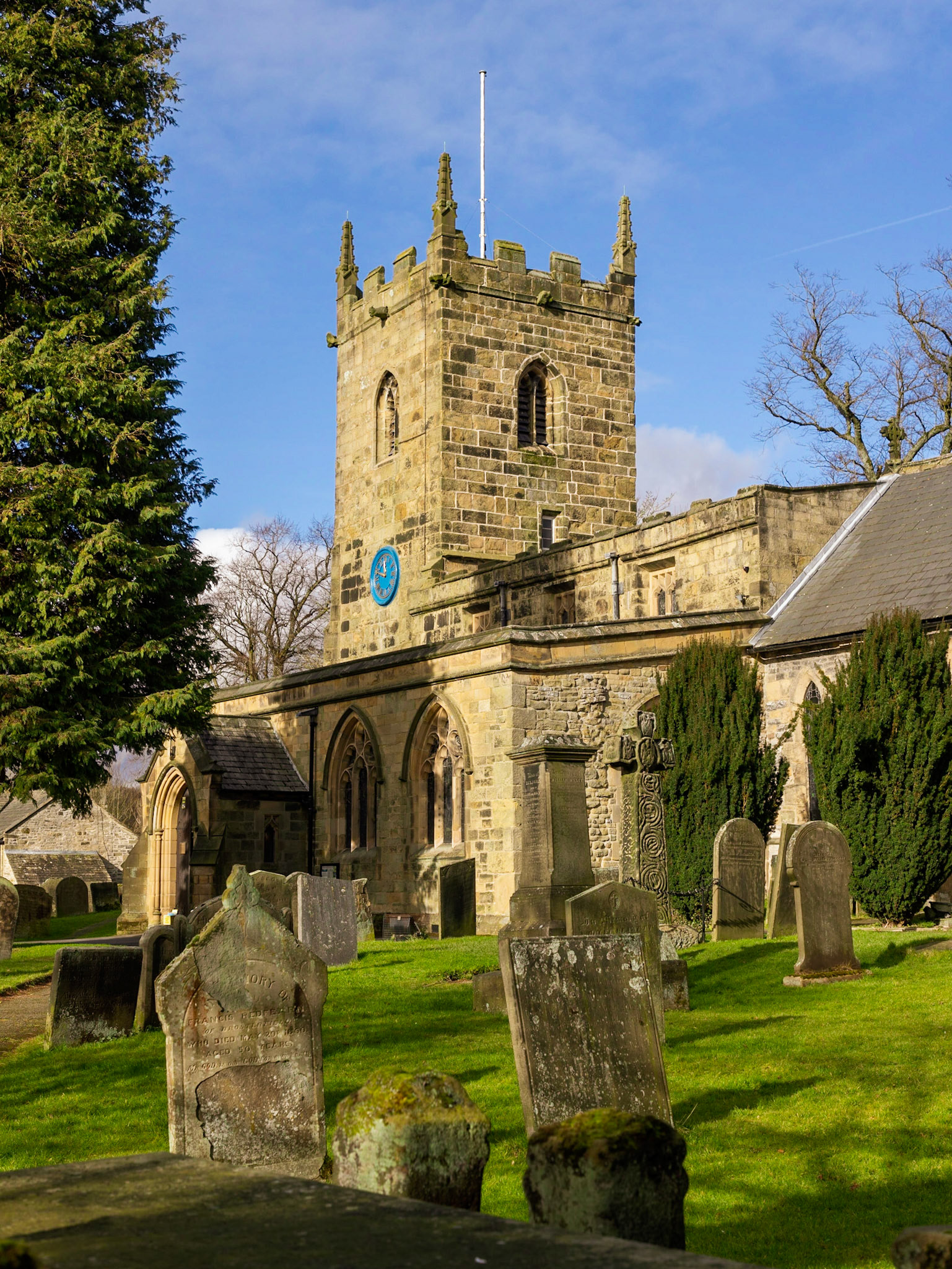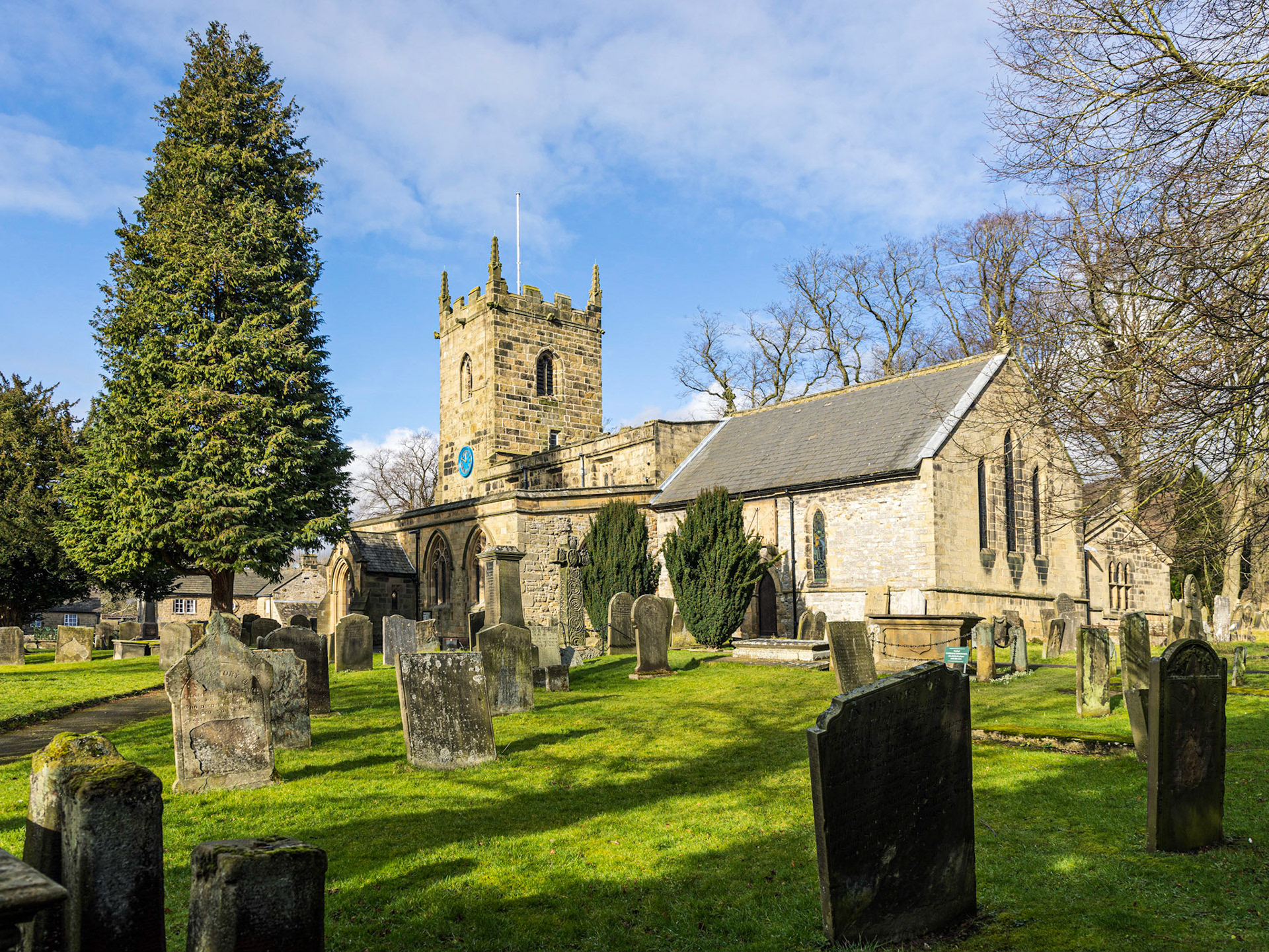
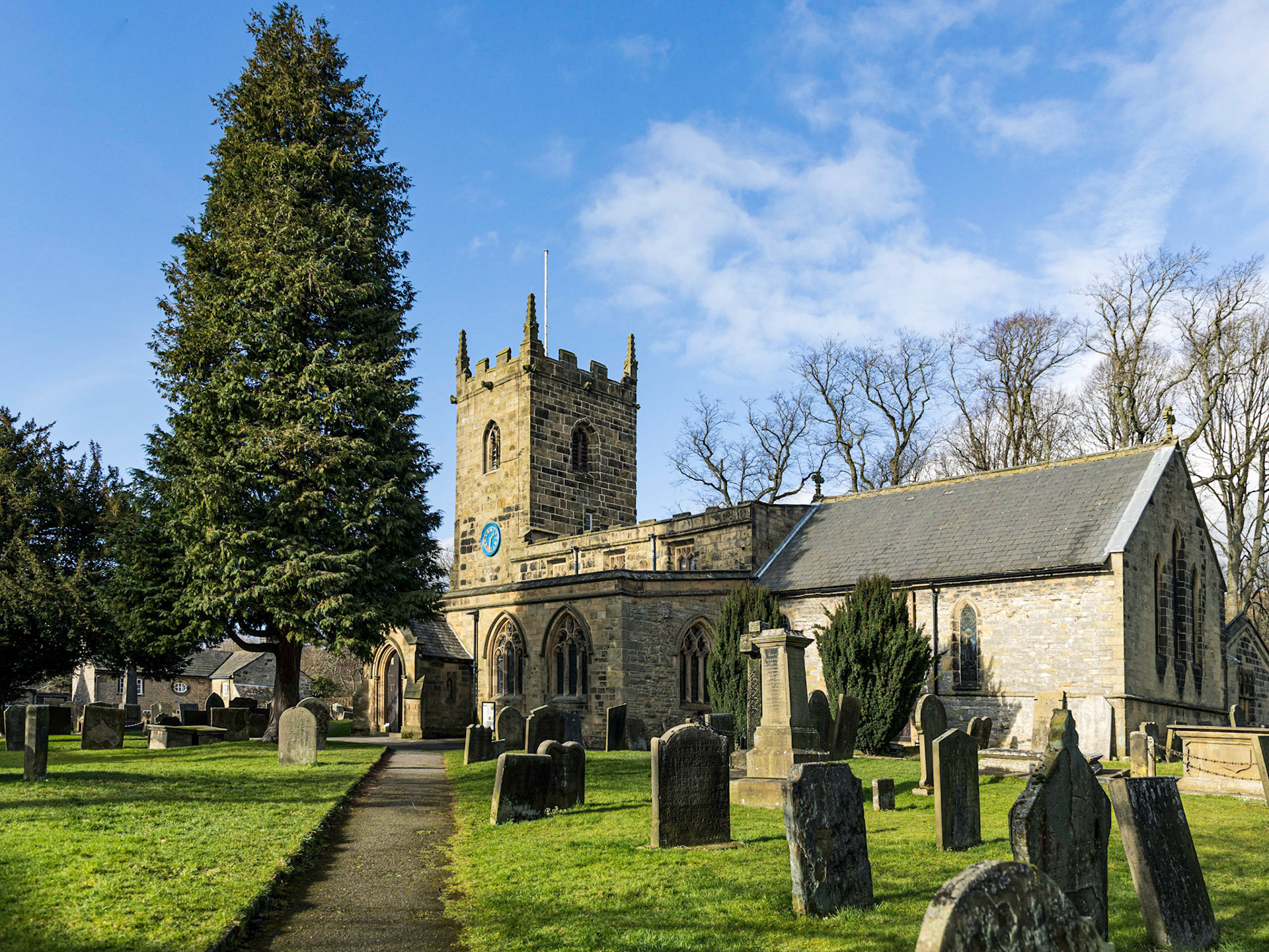
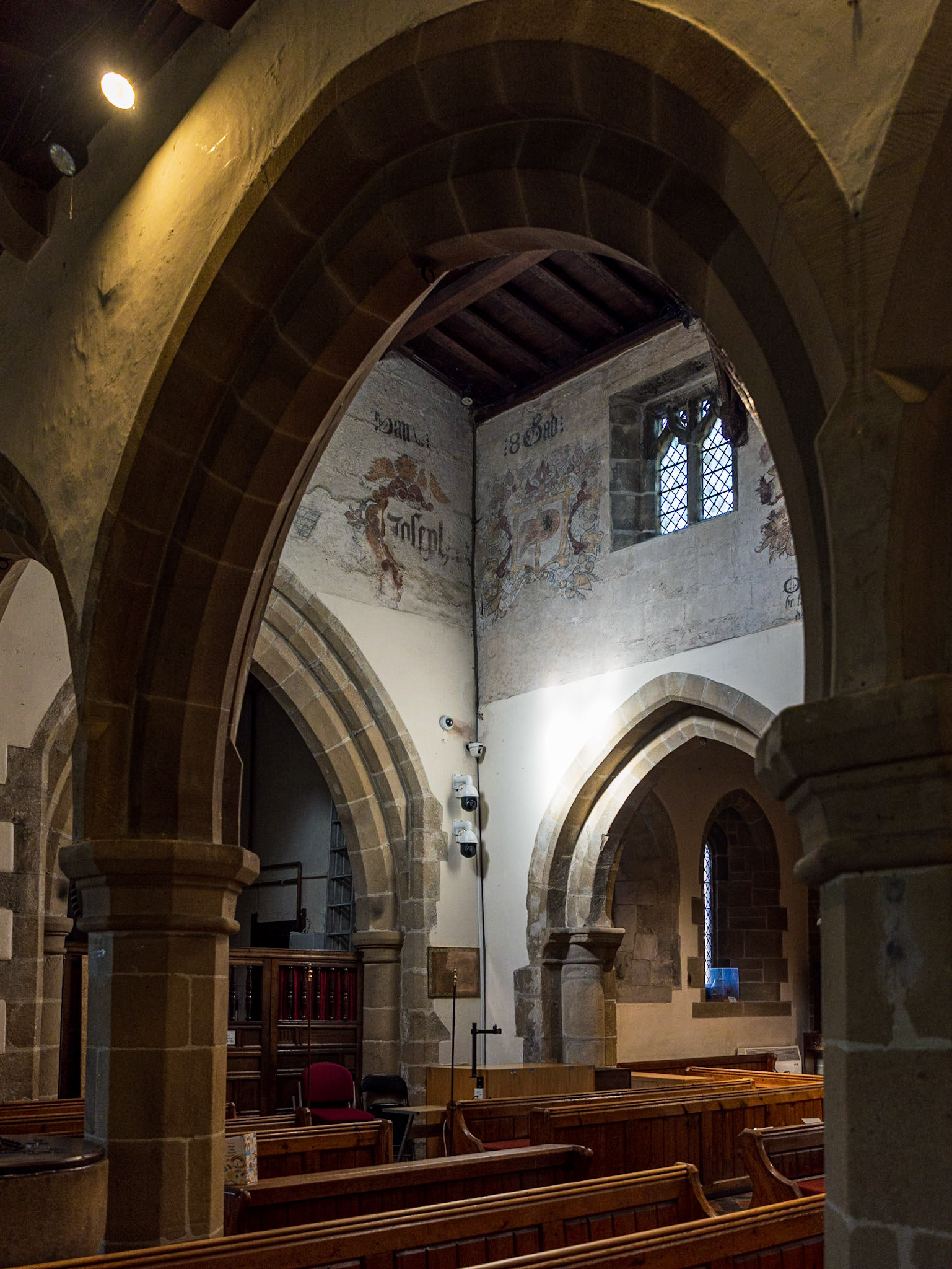
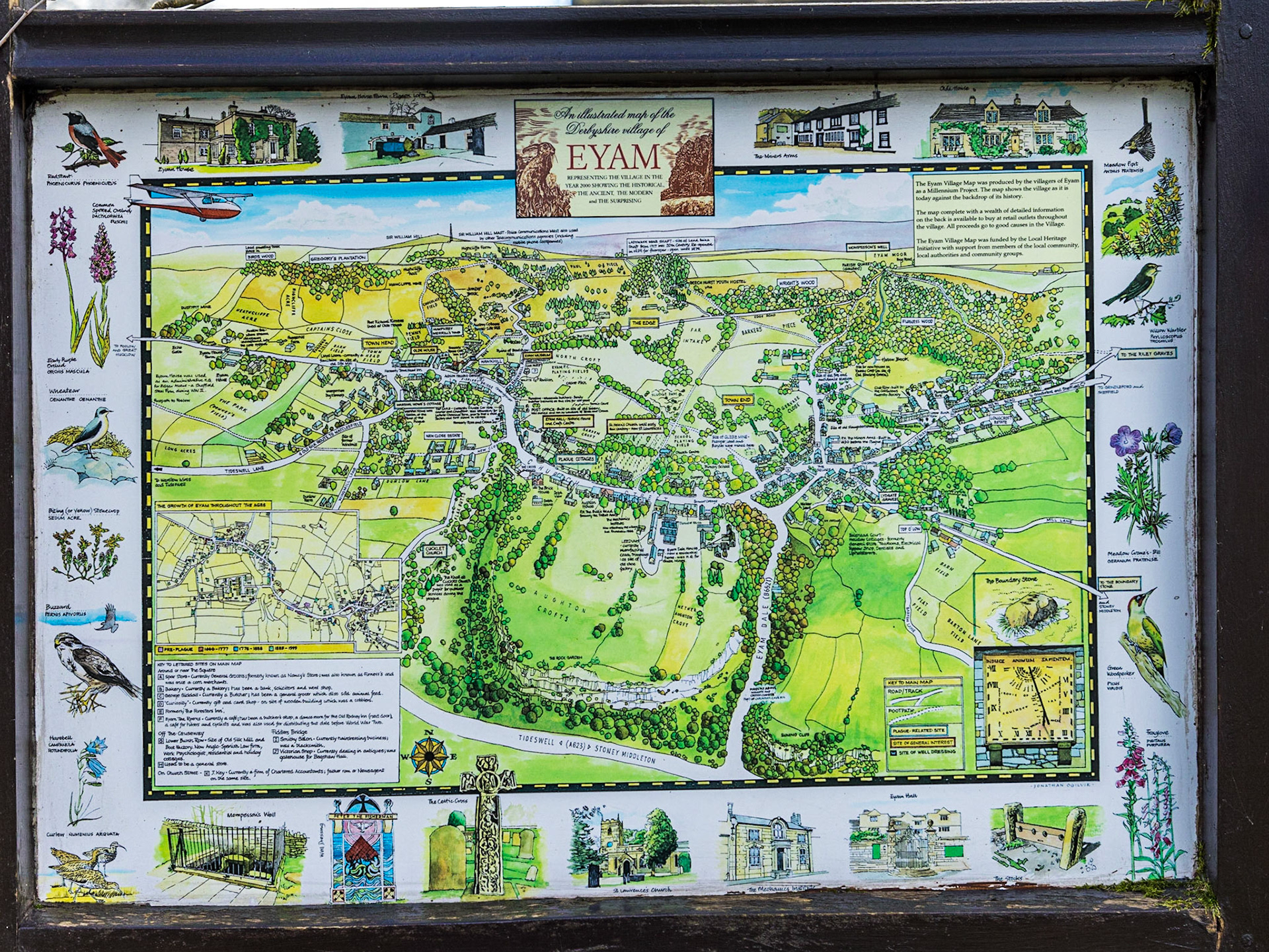
14th Century Parish Church of Saint Lawrence, Eyam

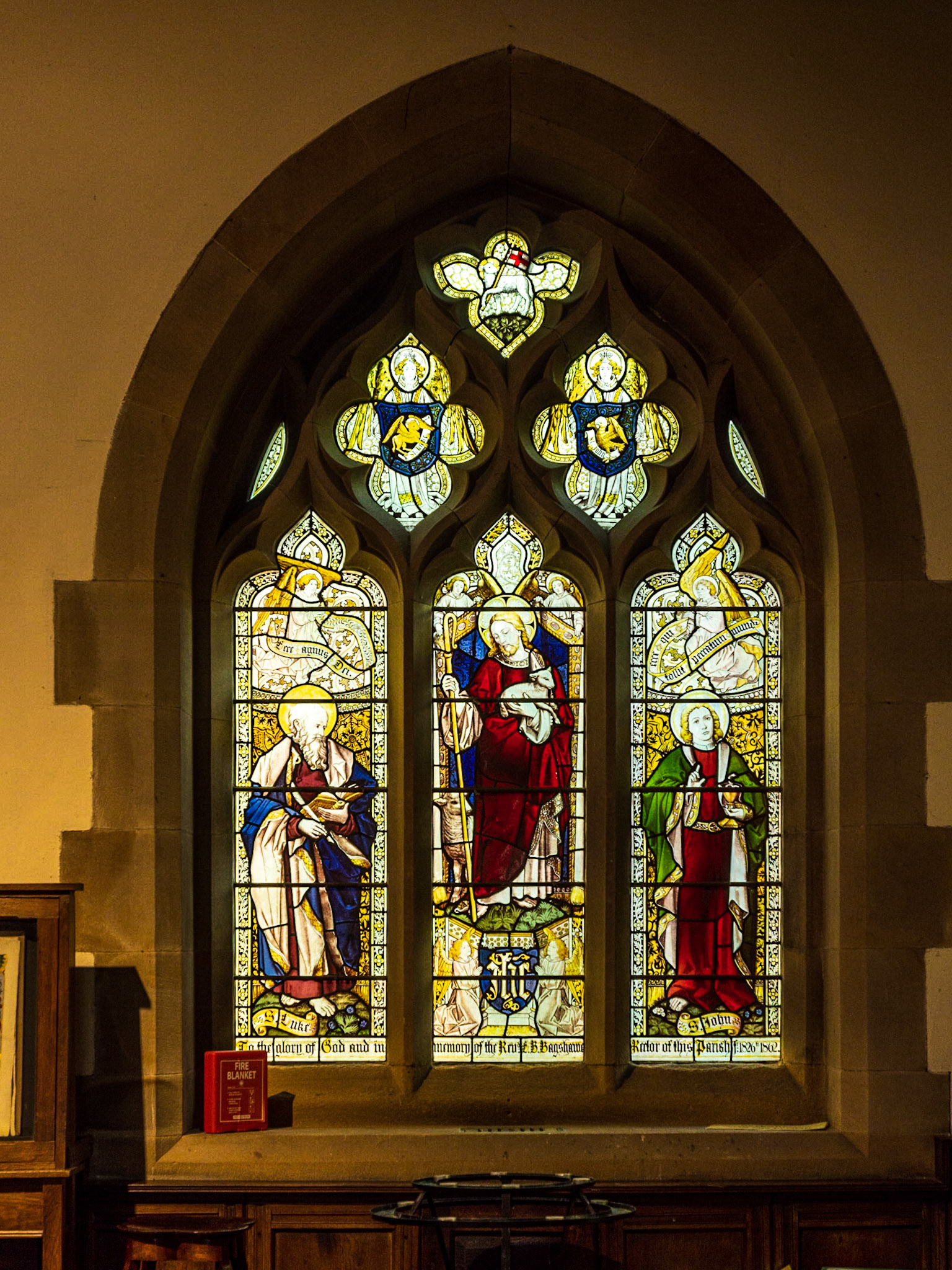
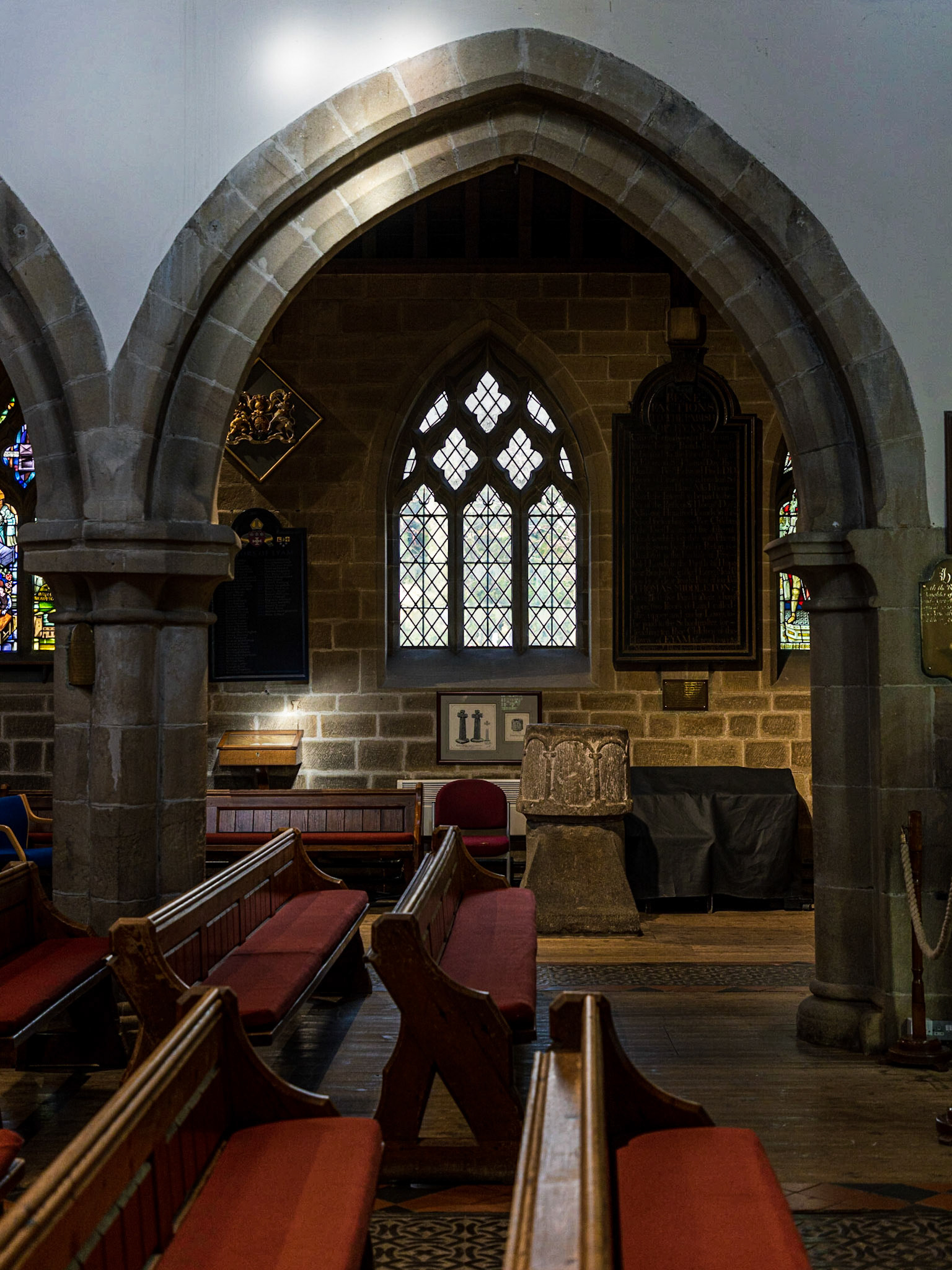
The Interior of the 14th Century Parish Church of Saint Lawrence, Eyam
![In the churchyard is an Anglo-Saxon cross in Mercian style dated to the 8th century, moved there from its original location beside a moorland cart track. Grade I listed and a Scheduled Ancient Monument,[9] it is covered in complex carvings and is almost complete, but for a missing section of the shaft.](data:image/gif;base64,R0lGODlhAQABAIAAAAAAAP///yH5BAEAAAAALAAAAAABAAEAAAIBRAA7)
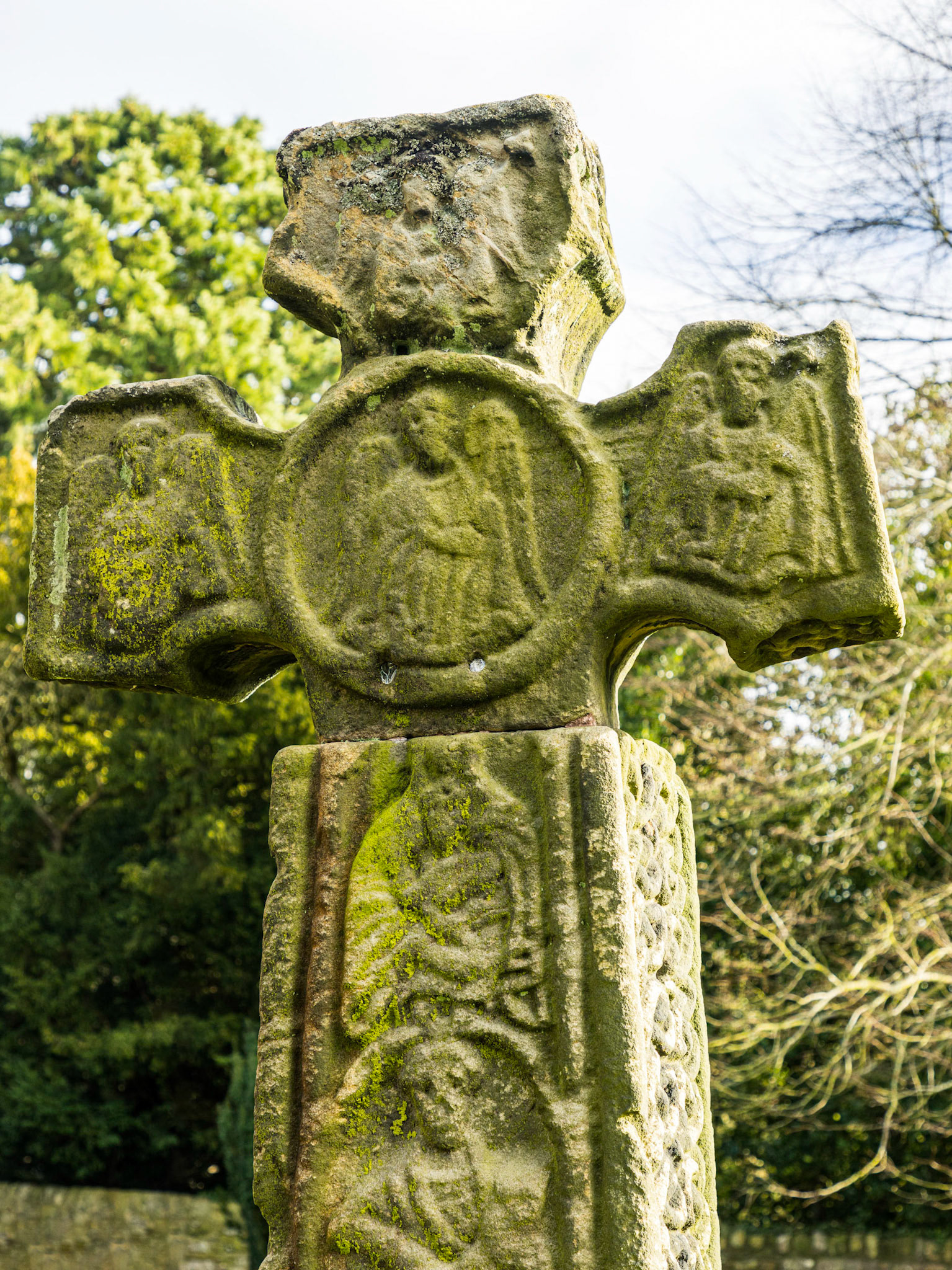
In the churchyard is an Anglo-Saxon cross in Mercian style dated to the 8th century, moved there from its original location beside a moorland cart track. Grade I listed and a Scheduled Ancient Monument,[9] it is covered in complex carvings and is almost complete, but for a missing section of the shaft.

In the churchyard at Eyam is an Anglo-Saxon cross in Mercian style dated to the 8th century, moved there from its original location beside a moorland cart track. Grade I listed and a Scheduled Ancient Monument, it is covered in complex carvings and is almost complete, but for a missing section of the shaft.

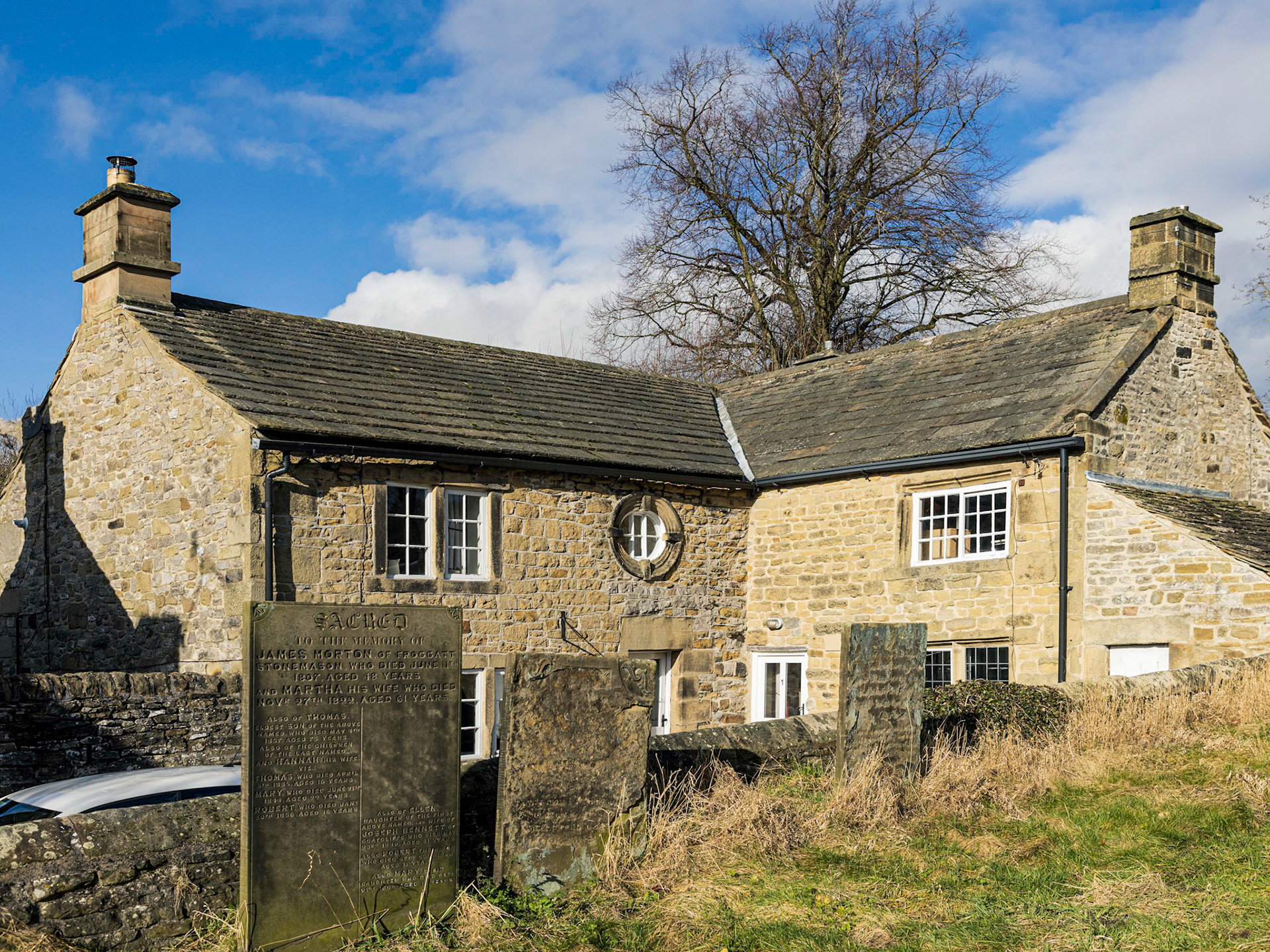
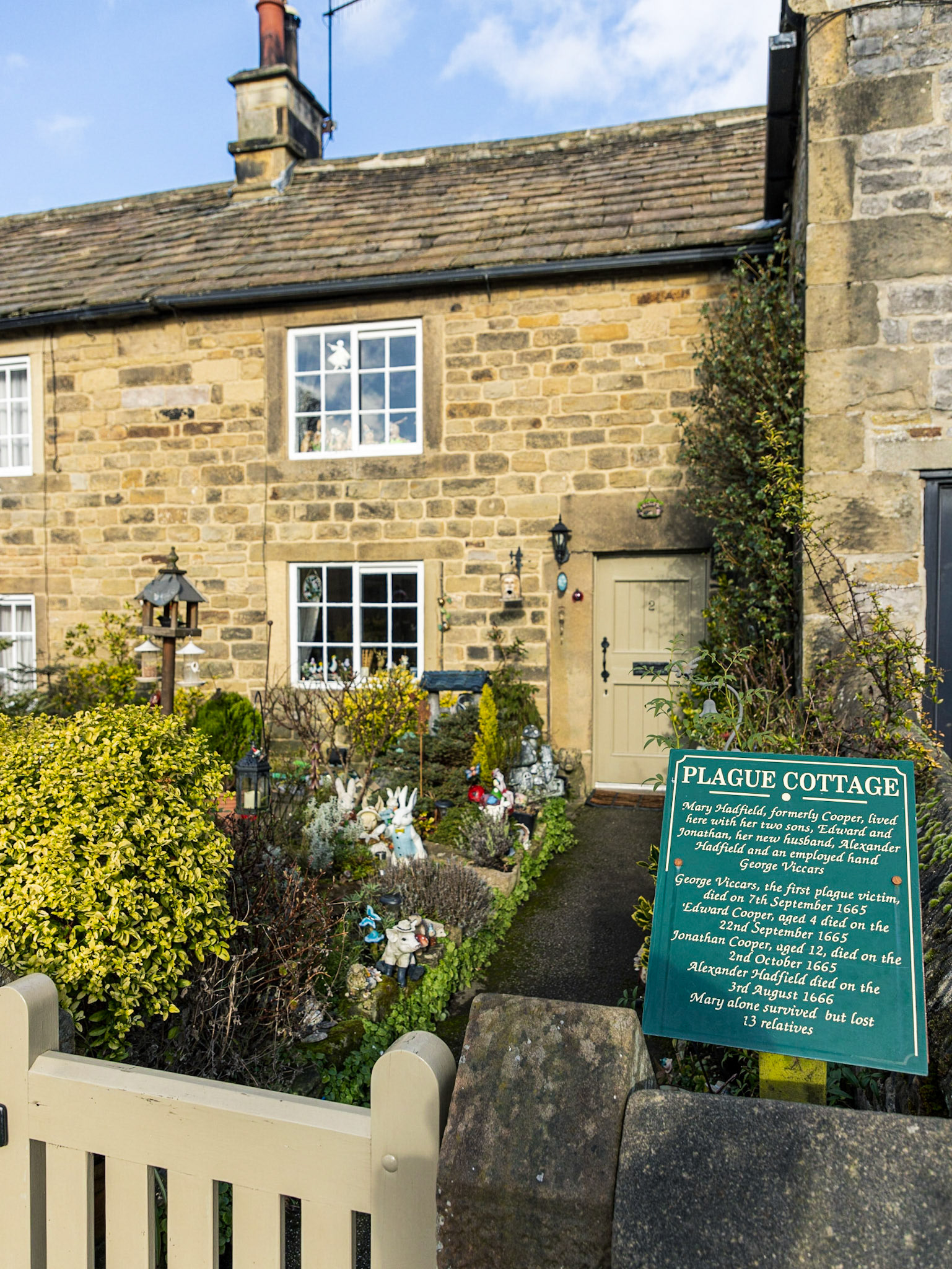
Old Cottages In Eyam adjoining the Churchyard

Sundial at Eyam Church

14th Century Parish Church of Saint Lawrence, Eyam










![In the churchyard is an Anglo-Saxon cross in Mercian style dated to the 8th century, moved there from its original location beside a moorland cart track. Grade I listed and a Scheduled Ancient Monument,[9] it is covered in complex carvings and is almost complete, but for a missing section of the shaft.](https://cdn.myportfolio.com/69730556-ec56-4978-b376-879eac0ff674/f535b3ef-a294-4151-b5d8-680af72eeb81_rw_1920.jpg?h=4993f1d4dcdeffc35b65a3f350307779)








